Commemoration of Africa Day of Peace and Reconciliation
Commemoration of Africa Day of Peace and Reconciliation
Date | 30 January 2025
Tomorrow (31 January), the African Union (AU) Peace and Security Council (PSC) will convene its 1258th session where it will discuss the third commemoration of the ‘Africa Day of Peace and Reconciliation’ as an open session.
Following opening remarks by Ennio Maes, Permanent Representative of the Republic of Cote d’Ivoire to the AU and Chairperson of the PSC for January 2025, Bankole Adeoye, Commissioner for Political Affairs, Peace and Security (PAPS), is expected to make a statement. Mr Domingos Miguel Bembe, Permanent Representative of the Republic of Angola to the African Union, may also provide a briefing on the efforts of Angola as the AU Champion for Peace and Reconciliation. Other members that may participate in the session include Lady Justice (Rtd) Effie Owuor, Judge of the Court of Appeals of Kenya and Chairperson of the AU Panel of the Wise, Welile Nhlapo, Senior Adviser to the African Centre for the Constructive Resolution of Disputes (ACCORD) and representatives from the UNOAU and the RECs/RMs.
The Commemoration comes immediately after the end of the ‘Madiba Nelson Mandela Decade of Reconciliation in Africa,’ which was declared to be from 2014 – 2024 and adopted through Decision [Assembly/AU/Dec.501(XXII)] by the 22nd Ordinary Session of the Assembly of the Union held on 30 and 31 January 2014 in Addis Ababa. We can also recall that during the 899th meeting held at the ministerial level on 5 December 2019, in Luanda, Angola, on the theme: ‘National Reconciliation, Restoration of Peace, Security and Rebuilding of Cohesion in Africa,’ in line with the Madiba Nelson Mandela Decade of Reconciliation in Africa, the PSC decided, among others, to ‘dedicate a session, once a year, aimed at experience sharing and lessons learning on national reconciliation, restoration of peace and rebuilding of cohesion in Africa; [a]nd to undertake a review of the implementation of the Madiba Nelson Mandela Decade of Reconciliation in Africa, based on the common African position on the review of the UN Peace Consolidation Framework to be developed by the AU Commission…’
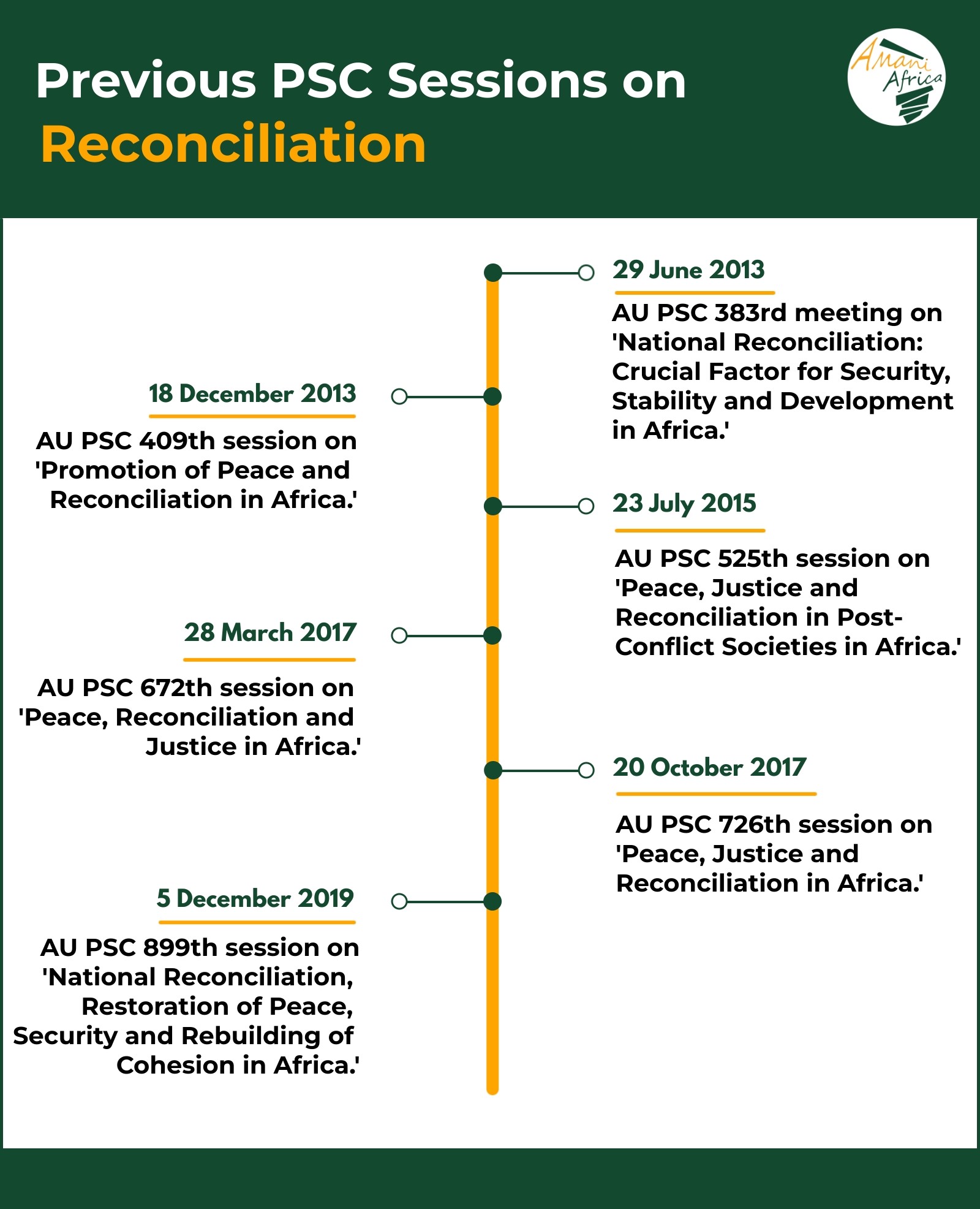
On 31 January 2024, the PSC convened for its 1198th meeting, in which it adopted the communiqué for the second Commemoration of Africa Day of Peace and Reconciliation. Expressing concern over ‘the deterioration of State institutions, the resurgence of unconstitutional changes of government and the outbreak of conflict in some Member States, including the growing threat of terrorism and violent extremism,’ Council underscored the importance of ‘justice in the reconciliation process as a fundamental pillar of peaceful and just societies’ and the need to ‘strengthen the pillars of the African Peace and Security Architecture (APSA) and the African Governance Architecture (AGA) to adequately address structural and cyclical instability…’ The concern that the PSC expressed during its last session continues to persist into this year. Tomorrow’s commemoration comes amidst the deteriorating security situation in Eastern DRC and the raging war in Sudan. The commemoration may thus serve as a platform to galvanise support for the Luanda and Nairobi peace processes, with the aim of improving coordination and clarifying responsibilities among the involved parties, including DRC and Rwanda, to implement peace agreements. The focus may highlight elements of inclusivity.
Tomorrow’s session, therefore, will seek to get an update on the efforts of the AU Champion for Peace and Reconciliation in supporting regional peace process efforts. The Luanda Process for mediating between DRC and Rwanda has registered notable milestones. Several rounds of talks at technical and ministerial levels produced, most notably, the signing of a ceasefire agreement, although it has not, in the end, prevented the recent upsurge in violence and escalation of conflict in Eastern DRC. It should also be recalled that on 27 June 2023, Angola hosted the ‘Quadripartite Summit of the East African Community (EAC), Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS), International Conference on the Great Lakes Region (ICGLR) and Southern African Development Community (SADC),’ in Luanda. The Summit adopted the ‘Joint Framework on Coordination and Harmonisation of Peace Initiatives in Eastern DRC by the EAC, ECCAS, ICGLR, SADC and the UN under the auspices of the AU’ which seeks to promote coherence of the existing peace initiatives of the Quadripartite in line with the relevant instruments and decisions with a clear division of responsibilities and agreed timelines. Following this, on 6 October 2023, the AUC convened the First Quadripartite Meeting of the Chiefs of Defence (CDFs) of the Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS), the East African Community (EAC), the International Conference of the Great Lakes Region (ICGLR) and the Southern African Development Community (SADC), as well as concerned countries of the DRC and the Republic of Rwanda on Coordination and Harmonisation of Regional Peace Initiatives in Eastern DRC. The meeting was convened to ensure coherence and harmonisation in the execution of existing peace initiatives in the region, in line with the decisions of the Quadripartite Summit held in Luanda on 27 June.
In this regard, fostering an inclusive reconciliation process that engages vulnerable groups such as women, youth and community leaders in alignment with the AU’s framework of ‘Silencing the Guns by 2030.’ Additionally, the humanitarian crisis, marked by widespread displacement and violations of human rights, may be underscored, with calls for enhanced humanitarian access and aid in conflict-prone situations. With the invitation of Lady Justice (Rtd) Effie Owuor as one of the presenters, the meeting is an opportunity to take stock of the AU’s achievements and leadership in mediation and peacemaking processes by highlighting the role of the AU Special Envoys, High Representatives, Panel of the Wise and other mediators in promoting dialogue, reconciliation and national healing. This is expected to culminate in proposing recommendations on enhancing cooperation and complementarity of efforts between the AU Champion, the PSC, the AU Commission and other actors on the Continent.
The expected outcome is a communiqué. The PSC is likely to applaud the efforts of H.E. João Manuel Gonçalves Lourenço, President of Angola and AU Champion for Peace and Reconciliation, for his unwavering commitment to fostering peace and reconciliation across the continent and for mobilising support for conflict prevention and resolution. It may call on all parties involved in any cessation of hostility agreements to fully commit to the implementation of such agreements, fostering trust and paving the way for lasting reconciliation, as well as all the reinforcement of AU mechanisms, including the Post-Conflict Reconstruction and Development (PCRD) frameworks and the Continental Early Warning Systems, to effectively address emerging conflicts and promote long-term stability. The council may also emphasise the importance of aligning the ‘Africa Day of Peace and Reconciliation’ with efforts to advance the implementation of the AU Transitional Justice Policy. The council may further highlight the imperative of further enhancing cooperation and complementarity of efforts between the AU Champion, AU High Representatives and Envoys, RECs/RMS and other actors on the Continent.
Exclusive interview: H.E. Amb. Bankole Adeoye, Commissioner for Political Affairs, Peace, and Security
Exclusive interview: H.E. Amb. Bankole Adeoye, Commissioner for Political Affairs, Peace, and Security
Jan 29, 2025
Update on the Operationalisation of the African Standby Force (ASF)
Update on the Operationalisation of the African Standby Force (ASF)
Date | 29 January 2025
Tomorrow (30 January), the African Union (AU) Peace and Security Council (PSC) will convene its 1257th session with two agenda items. Following the Consideration of the Report of the Activities of the Peace and Security Council and the State of Peace and Security in Africa; and the Report on the implementation of the AU Master Roadmap of Practical Steps to Silencing the Guns in Africa: Achievements, Challenges and Prospects, the Council will receive Updates on the status of the operationalisation of the African Standby Force (ASF).
Following the opening statement of the Chairperson of the PSC for the month of January, Ennio Maes, Permanent Representative of the Republic of Cote D’Ivoire, Bankole Adeoye, the Commissioner for Political Affairs, Peace and Security (PAPS), is expected to present the progress made in the operationalisation of the Force with a specific focus on the steps undertaken to facilitate the consultative process for the Strategic Review of the ASF.
The ASF, envisioned under Article 13 of the PSC Protocol as a cornerstone of the African Peace and Security Architecture (APSA), was designed to serve as Africa’s primary mechanism for peace support operations (PSOs) and crisis intervention. Despite being declared fully operational in 2015, the ASF continues to face significant challenges, particularly in political coordination, logistical readiness, and rapid deployment capabilities.
The last time the PSC convened on the ASF was during its 1159th session held at the ministerial level on 22 June 2023, where it requested the AU Commission, among other things, to expedite ‘the strategic review of the ASF in order to align it with contemporary security challenges facing the continent’ drawing on Conclusions of the Inaugural Lessons Learned Forum on AU Peace Support Operations that was held in November 2022, in Abuja, Nigeria and subsequently adopted by the Council. Previously, the PSC, in its 1129th session, had also requested the Commission to use the identified lessons in reviewing and reconceptualising the ASF Concept, with a view to ensuring its alignment with the AU Doctrine on PSOs and to ensure the readiness of the ASF to address the contemporary complex, multifaceted and dynamic peace and security challenges facing Africa. The process seeks to ensure that the ASF remains fit for purpose while ensuring its integration with the AU’s peace support operations doctrine.
It is expected that in tomorrow’s session the Commission will provide updates regarding the engagements it had with key stakeholders for the strategic review of the ASF. It is to be recalled that the Commission had held a technical consultative meeting with ASF RECs/RMs Planning Elements (PLAMELMs), strategic partners and subject matter experts and resources persons in in Algiers from 2-4 December 2024.
A major impediment to the ASF’s operationalisation has been the lack of political consensus and institutional alignment between the AU and Regional Economic Communities/Regional Mechanisms (RECs/RMs). While the adoption of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) during the 15th Specialised Technical Committee on Defence, Safety, and Security (STCDSS) in May 2023 was a step forward that clarified roles and responsibilities in planning, deployment, and post-deployment stages, it has not fully resolved underlying tensions. Political sensitivities, including competing interests among RECs, continue to impede seamless coordination. This misalignment complicates decision-making and affects the ASF’s ability to plan, deploy, and manage missions efficiently. The ASF’s operational readiness requires clear frameworks and greater harmonisation of roles and responsibilities under AU leadership.
The ASF’s readiness varies across regions. While the Southern African Development Community (SADC) and the Eastern Africa Standby Force (EASF) have made substantial progress, other regions face ongoing challenges that include resource shortages and limited coordination, which are exacerbated by debates over the balance of authority between RECs and the AU. ECOWAS, for instance, has expressed a strong desire to retain control over deployments within its jurisdiction, creating potential conflicts with the AU’s broader coordination role. It is expected that tomorrow’s session will take an interest in enhancing coordination between the Planning Elements (PLANELMs) of the RECs/RMs and the Continental PLANEL in order to facilitate harmonisation of decision-making on the deployment of the ASF based on the principles of subsidiarity, complementarity and comparative advantages to ensure that the ASF can operate as a unified and effective force. To this effect, the AU Commission has held consultations with the five ASF PLANELMs, including EASF, ECCAS, ECOWAS, SADC and NARC, on 5 December 2024 in Algiers.
Logistical readiness also remains another significant obstacle to the ASF’s operationalisation. The establishment of the Continental Logistics Base (CLB) in Douala, Cameroon, in 2018 was a step forward, but the incomplete development of Regional Logistics Depots (RLDs) continues to hinder the ASF’s capacity for rapid deployment. Strategic airlift capabilities, vital for moving troops, equipment, and supplies, also remain inadequate. Recognising this gap, the PSC’s 1159th session had requested the AU Commission to expedite the assessment exercise of pledged strategic lift aircraft as part of efforts to enhance strategic lift capability and the finalisation of the agreements for the utilisation of the pledged strategic lift assets to enable ASF rapid deployment of troops, reinforcement of troops, casualty evacuations and timely logistic supplies in conflict zones. The ASF’s maritime readiness is also another area requiring attention as preparations for the first ASF maritime exercise are undergoing progress, but further investment is still required to establish a robust maritime component within the ASF. On the Continental Logistics Base, while welcoming the structures approved by the 36th ordinary session of the Assembly, the PSC may appeal to Member States to support the efforts for the mobilisation of the required budget of USD 4,717,606.45 for the approved structures.
In the context of the shift in the nature of conflicts with conflicts involving terrorist groups having become dominant in recent years, the ASF’s potential role in counter-terrorism is another area of strategic importance. The growing threat of terrorism and violent extremism across the Sahel, Horn of Africa, and other regions necessitates adapting the assumption that underpinned the conception of the ASF with its focus on intra-state conflicts. This has prompted questions on the need for specialised and rapid-response capability. It was against this background that the PSC adopted a decision to establish a counter-terrorism unit within the ASF during its 960th session in October 2020, which remains a key priority. Tomorrow’s session will also present an opportunity to follow up on this decision.
Despite the challenges it faces, the ASF framework offers an unparalleled opportunity for standardising training, enhancing interoperability, and building institutional resilience across Africa’s security architecture. Many troops have benefited from ASF-led training programs, which have built a shared understanding of operational procedures and improved readiness. While RECs and ad hoc arrangements have often deployed peace support operations independently, integrating such initiatives into the ASF framework will enhance collective security efforts and optimise resources.
In terms of follow-up on the request for a strategic review of the ASF, including by the PSC, initial steps were taken last December with the convening of the meeting in Algeria. The consultative meetings held in Algiers, Algeria, which included the Technical Consultative Meeting on the ASF and consultations with ASF RECs/RMs, have been centred around the themes of legal and policy framework of the ASF, the political challenges facing its operationalisation, securing predictable and sustained financing, operational challenges facing ASF and mechanisms to enhance the capacities of ASF. However, the AU Commission claims that the strategic review process of the ASF continues to face delays due to funding gaps. One way of overcoming this is to leverage the Network of Think Tanks for Peace that the PAPS department assembled.
Efforts to develop the ASF’s cost-sharing model must continue, as this approach promotes joint regional solutions and shared responsibility in addressing security challenges. By refining this model, the ASF can encourage greater financial commitment and ownership among member states and RECs/RMs. The efforts in collective resource mobilisation and sharing need to be aligned with the legal expectations of the PSC Protocol. The AU also needs to seize the opportunity that Resolution 2719 presents in affirming the central role of the AU and its leadership as envisaged in the PSC protocol in the deployment of peace support operations.
The PSC’s directive to integrate ASF principles into all AU peace support operations represents a significant step toward institutionalising the framework. Moreover, the alignment of the ASF’s concept with the AU’s doctrine on PSOs would ensure that its operations are guided by a coherent strategic vision. As Africa faces increasingly complex and multifaceted security threats, the ASF remains an indispensable tool for promoting peace and stability.
The ASF remains central to realising the vision of African-led peace and security, but its potential can only be fully realised through concerted efforts to overcome its enduring challenges. As the PSC deliberates on the ASF’s future, it must prioritise ensuring unity of purpose among AU member states and RECs, ensuring that the ASF serves as a symbol of African solidarity and a practical mechanism for achieving peace and security.
The expected outcome of tomorrow’s session is a communique.
Emergency ministerial meeting on the current escalation of the conflict in Eastern DRC
Emergency ministerial meeting on the current escalation of the conflict in Eastern DRC
Date | 27 January 2025
Tomorrow (28 January), the African Union (AU) Peace and Security Council will convene an emergency ministerial level session on the conflict in Eastern Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). The session is convened following a letter sent from the DRC requesting for the PSC to convene urgent meeting on the deteriorating security situation in Eastern DRC. The meeting is scheduled for 4 pm East African Time.
The session is expected to commence with opening remarks from Kacou Houadja Leon Adom, Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Cote d’Ivoire and Chairperson of the Peace and Security Council of the African Union for the Month of January 2025. Bankole Adeoye, Commissioner for Political Affairs, Peace and Security (PAPS), is expected to make a presentation on recent developments and the current escalation of the conflict. Apart from the DRC, which is a member of the PSC and will address the PSC as a country concerned, it is anticipated that Rwanda will also deliver a statement as a country concerned. The PSC will also hear statements from the representatives of Angola, in its capacity as the Chairperson of the International Conference of the Great Lakes Region (ICGLR), Tanzania, in its capacity as Chairperson of the Southern Africa Development Community (SADC) Organ, Kenya, in its capacity as Chairperson of the East African Economic Community (EAC). Additionally, PSC is also expected to receive an update from the Special Representative of the Secretary-General in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Head of the United Nations Organisation Stabilisation Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (MONUSCO).
Tomorrow’s session comes against the background of the escalation and expansion of fighting involving the M23 armed group. After opening a new front in South Kivu and capturing the town of Masis in North Kivu province early in the month, the M23 made further advances. The rebel group captured Kalehe on 19 January and Minova on 21 January. During the past three days, it encircled the capital of North Kivu, Goma. The fighting escalated following the killing of the Governor of North Kivu and the seizure by the M23 of the strategic town of Sake, 27 kilometres from Goma, on 23 January. The UN reported that the flareup of fighting has led to, among other humanitarian consequences, the displacement of over 400,000 people.
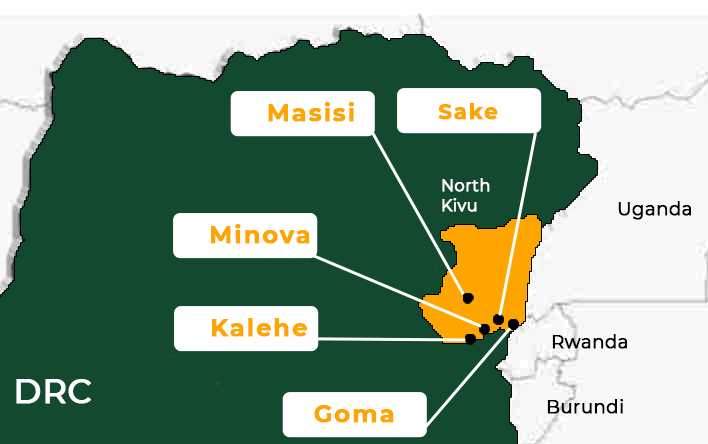
The fighting during the past few days, centred around the surroundings of Goma, was heavy. After encircling Goma and closing its airspace, on Sunday, the rebel group issued an ultimatum to the DRC Army (FARDC) demanding their surrender by 3:00 am, following which it ‘will proceed to occupy the city of Goma.’ On Monday morning, Goma fell into the hands of the M23. It is reported that some Congolese forces have continued to put up some resistance, while hundreds of FARDC soldiers surrendered to UN peacekeepers. Dozens of other Congolese soldiers also reportedly fled to Rwanda. MONUSCO staff and their families also crossed into Rubavu and have since arrived in Kigali by busses carrying them.
Since the fall of Goma, tensions have escalated on the border. Rwanda reported that bomb shells launched from the DRC led to the killing of 5 and injured 35 others on the outskirts of Rubavu town, prompting the closure of civilian activities, including schools and shops in Rubavu near the border. Reporters from Goma also indicated hearing drones and mortars/artillery coming from Rwanda. These are worrying signs of risk of the situation escalating into a direct confrontation between the two countries.
Ahead of the fall of Goma, heavy fighting took place as SAMIDRC and MONUSCO, along with FARDC, sought to halt the advance of the M23 toward Goma. It was as part of its Operation Springbok launched in November 2023 that MONUSCO engaged in attempting to forestall the M23’s march for seizing Goma. While the UN reported earlier that two MONUSCO peacekeepers have died, and nine others sustained injuries during the latest offensive, which started on 23 January, Urugua also reported the death of one of its soldiers. Three Malawian soldiers were also killed. SAMIDRC also sustained the loss of life of its personnel. The South African National Defence Force (SANDF) announced that it lost nine soldiers in the latest offensive, with seven of them serving under SAMIDRC and two others under MONUSCO. The statement from SANDF that ‘the South African contingent and its counterparts were able to halt the advancement of the rebel group towards Goma’ did not last long, as Goma fell into the hands of M23 two days later.
The current escalation that accelerated in the course of this month followed the collapse of the summit-level meeting of the Luanda Process under which the DRC and Rwanda have held a series of ministerial talks, whose outcomes include the signing of a ceasefire that came into effect in August 2024. The summit, involving a face-to-face meeting between Congolese President Félix Tshisekedi and Rwandan President Paul Kagame in Luanda under the facilitation of Angola’s President Jaoa Manuel Lorenço on 15 December 2024, was postponed ‘at the request of one of the parties at the last minute’, according to a statement by Angola’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs. While DRC’s President Tshisekedi travelled to Luanda in anticipation of the summit talks, his counterpart Rwanda’s Kagame canceled his travel at the last minute as he told journalists during his press briefing on 9 January. The postponement of the tripartite summit was attributed to the divergent views registered regarding the resolution of the M23 issue during the ministerial meeting held on 14 December ahead of the summit. In a letter it sent to the UN Security Council on 17 December accusing Rwanda of causing delay by insisting on direct negotiations with M23, DRC stated that it has no objections to the participation of the M23 in the Nairobi process, the EAC-led peace process headed by former Kenyan President Uhuru Kenyatta. Rwanda rejected the accusation in a counter letter it sent on 19 December, stating that the issue of the M23 has been included by the facilitator in the draft agreement presented to the two countries in August 2024.
It is to be recalled that the M23 was defeated after it seized Goma for a week in 2012 but resurfaced again three years ago. Since the resumption of its overt military activities in March 2022, M23 has been able to advance and capture key strategic towns in Kivu and Ituri provinces. Although M23’s activities became widely apparent in March 2022, reports indicate that the movement has been infiltrating key military positions and strategic areas in North Kivu since at least November 2021. In May 2022, during the 16th Extraordinary Summit of the AU, the AU Assembly designated Angola’s President Lorenço to be the facilitator for talks between Rwanda and DRC. While it has registered some gains, including avoiding the descent of the two countries into direct war and a ceasefire signed in July 2024, it ran into a deadlock in December 2024, as highlighted above.
Rwanda’s disaffection with the Luanda process was also implicitly revealed during a press conference that President Kagame held on 9 January. He told journalists that ‘we have processes and leaders leading these processes’ and ‘what becomes more important is the appearance, camera appearance, it is being seen there to be signing something and that becomes an end itself,’ underscoring that what matters is the substance and addressing the problems. At the same time, he stated that the process has to continue, but ‘it cannot be business as usual’ putting process above the results, despite the fact that Turkïye’s President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan reportedly offered to mediate between DRC and Rwanda after a meeting with his Rwandan counterpart who was on an official visit in Turkïye.
The panic and state of fear that the fall of Goma gave rise to prompted a flurry of diplomatic reactions and activities from various quarters. Angola’s President Lourenço issued a statement on 24 January, expressing deep concern over the deterioration of the security situation and strongly condemning the ‘irresponsible actions of the M23 and its supporters who endanger all efforts and progress achieved in the Luanda process’. The following day, AU Commission Chairperson, Moussa Faki Mahamat, issued a statement expressing deep concern and calling for ‘strict observance of the ceasefire agreed between the parties and the immediate cessation of all hostilities.’ DRC expressed its indignation at the description in Mahamat’s statement of the M23 as a ‘politico-military opposition’. On that same day 25 January, the SADC Secretariat issued a statement expressing concern and condemning the recent attack on SAMIDRC by the M23. The UN Secretary-Genera, in a 23 January statement, condemned the renewed offensive by the M23, including the capture of Sake and called on the group to stop its offensive, withdraw from all occupied areas and abide by the 31 July 2024 ceasefire agreement signed between DRC and Rwanda under Angola’s facilitation. He further stated, ‘he is troubled by the most recent report of the Group of Experts established pursuant to Security Council Resolution 1533, concerning the presence of Rwandan troops on Congolese soil and continued support to the M23.’
As the M23 advance toward Goma persisted despite attempts to halt it, the UN Security Council (UNSC) emergency session, which was initially scheduled for Monday 27 January, was moved to Sunday, 26 January. During her briefing to the UNSC, Bintou Keita, Special Representative of the Secretary-General for the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Head of MONUSCO ‘called on Rwanda to withdraw its forces from Congolese territory and end support for M23 and on the Democratic Republic of the Congo to ‘make significant efforts’ to neutralise the Democratic Liberation Forces of Rwanda, or FDLR.’ The three African members of the UNSC (A3 plus), in a joint statement delivered by Sierra Leone during the briefing, stated that the ‘resolution of the conflict in eastern DRC [Democratic Republic of the Congo] must be political, not military, while underscoring that the sovereignty and territorial integrity of the Democratic Republic of the Congo must be respected ‘by all States and non-State actors alike’. While the interventions from various UNSC members also asserted the imperative for respecting DRC’s sovereignty and territorial integrity and urged the withdrawal of support for M23, Rwanda’s representative told the UNSC that ‘the current crisis could have been averted had the DRC Government demonstrated a genuine commitment to peace.’ The UNSC subsequently issued a press statement, which, among others, condemned ‘the ongoing flagrant disregard for the sovereignty and territorial integrity of the DRC, including the presence in the Eastern DRC of external Forces’ and ‘demanded that these forces withdraw immediately and that the M23 put an end to the establishment of parallel administrations in the DRC territory .’
As the PSC convenes tomorrow, it faces the heavy and diverse ramifications of this dire situation. There are concerns that the current situation may push the DRC and Rwanda into full-blown direct conflict. Additionally, there are also understandable concerns about the heightened risk of the situation degenerating into a wider regional conflict, with the loss of lives involving peacekeepers from Southern Africa and the reported presence of forces from Burundi fighting on the side of DRC. These developments necessitate urgent de-escalation initiatives by the AU and regional bodies. Apart from interrupting the operation of the UN, including its peacekeeping mission, the fighting in Goma has curtailed humanitarian access and activities. Further to heightening inter-communal tension and violence, it is also forcing a large number of people into displacement.
The expected outcome of the session is a communiqué. The PSC is expected to condemn the violation of the ceasefire agreement signed under the Luanda Process and the recent escalation of fighting involving the M23. It may accordingly reiterate its call for unconditional cessation of hostilities and the withdrawal of the M23 from areas it has occupied. It may also urge for the follow up of the discussions under the Lunda Process for the neutralisation of the FDLR. The PSC may call for the establishment of a joint mechanism of the quadripartite framework for the monitoring of the ceasefire that came into effect in August 2024. It is also expected to call for respect of the sovereignty and territorial integrity of the DRC and restate its call for the withdrawal of all foreign forces operating in DRC. It may also welcome the statement of the UN Security Council and urge all actors to adhere to the demands of the statement. It PSC may urge Rwanda and DRC to refrain from actions that further aggravate the situation and accelerate risk of direct confrontation. Following the A3, the PSC may affirm that there is no military solution to the conflict and a political solution on the basis of the Luanda Process is the only viable option for its full resolution. The PSC may call for urgent dispatching of a high-level delegation of Heads of State and Government drawn from AU, EAC and SADC to Kinshasa and Kigali for urgent implementation of de-escalation measures and facilitating the return of the parties to the Luanda Process. The PSC may also urge restoration of calm, protection of people fleeing the affected areas and provision of humanitarian access.
